PV277 Programming Applications for Social Robots
[ previous part ] [ next part ]
How to get info from web?
Remember that Python usage in Pepper robots is limited to Python 2 and old versions of packages. It is possible to install some (small) Python packages via pip --user to /home/nao but the space is limited.
If you want to test without the real robot, you can run the Python 2 code (in or outside Choregraphe) using the virtual robot - see below.
Use website API
If API exists, you can usually use JSON data after send the right parameters. Example to get weather data.
import requests
url = "http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather"
params = {'q': 'Brno',
'units': 'metric',
'lang': 'cz'}
r = requests.get(url=url, params=params)
data = r.json()
print(data['main']['temp'])
(Full example forecast.py )
HTTPS problems
Note: some websites may limit the https access to newer versions of the SSL protocol, which may result in errors like error:14077410:SSL routines:SSL23_GET_SERVER_HELLO:sslv3 alert handshake failure. In such case, you may try to update the requests and pyOpenSSL packages in the Choregraphe Python using ($PEPPER_ROOT comes from installation instructions):
sudo $PEPPER_ROOT/pyenv/bin/pip2 install --target='/opt/Softbank Robotics/Choregraphe Suite 2.5/lib/python2.7/site-packages' \
requests==2.18.4 pyOpenSSL==19.0.0
Problems with wrongly recognized certificates can be usually solved in Python with
import urllib3.contrib.pyopenssl
import certifi
import urllib3
urllib3.contrib.pyopenssl.inject_into_urllib3()
http = urllib3.PoolManager(cert_reqs='CERT_NONE', ca_certs=certifi.where())
text = http.request('GET', url).data.encode('utf-8')
Parse webpage data
If no API is provided, you can download and parse the webpage.
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
page = requests.get(url).text
soup = BeautifulSoup(page, features="lxml")
results = soup.findAll('h3', attrs={'class':'article-title'})
(Full example news.py)
In virtual robot, if you get a runtime error: No module named bs4, you may need to install the package into the Choregraphe environtment via ($PEPPER_ROOT again comes from installation instructions):
sudo $PEPPER_ROOT/pyenv/bin/pip2 install --target='/opt/Softbank Robotics/Choregraphe Suite 2.5/lib/python2.7/site-packages' \
beautifulsoup4==4.9.3
Use pip instead of pip2 in older linux systems.
Beware that the version of just installed bs4 package may be different from the version on the real robot (but 4.9.3 is the last version supporting Python 2).
A safe option to include new packages is to install the package (e.g. yourmodule) in the application directory (e.g. lib) and import it like:
def __init__(self):
GeneratedClass.__init__(self)
self.folderName = os.path.join(self.behaviorAbsolutePath(), "../lib")
def onInput_onStart(self):
if self.folderName not in sys.path:
sys.path.append(self.folderName)
import yourmodule
# ... use yourmodule
if self.folderName in sys.path:
sys.path.remove(self.folderName)
self.onStopped() #activate the output of the box
Load local data
The same approach may be used for accessing your own data (e.g. in csv or json format) stored within your application directory. You need to include the file within the app package description ....pml file as:
<Resources>
<File name="data.csv" src="data" />
</Resources>
and load it in a Python box with correct path
import csv
class MyClass(GeneratedClass):
def __init__(self):
GeneratedClass.__init__(self)
self.folderName = os.path.join(self.behaviorAbsolutePath(), "..")
self.data = []
with open(os.path.join(self.folderName, 'data.csv'), 'rb') as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
self.data.append(row)
self.logger.info("data: %d rows loaded" % len(self.data))
How to integrate info with robot?
There are 2 basic options:
- use simple dialog variables as input and say the results directly in the Python script
- use complex service (=a separate Python class/script) which fully integrates in the Pepper API
These options are detailed below.
Option 1 - Dialog variables
In the dialog topic file, set a value of a variable, use the variable in a Python script in the robot's behavior. See the example application below for details.
concept:(team) [sparta spartě slavie slavii]
u:(["Můj [oblíbený nejoblíbenější] tým je" "Fandím {týmu}"] _~team) $team=$1
First word after sentence is available in $1 and passed to the script as team variable.
def onInput_onStart(self, team):
self.team_name = 'Slavia'
if ((team.lower().startswith('spart')):
self.team_name = 'Sparta'
Use TTS in script
# find out self.team_points for self.team_name from web sentence = self.team_name + " má " + str(self.team_points) + " bodů" self.tts.say(sentence)
Option 2 - Run script as service and parse service output
Specify service script in manifest.xml (here rozvrh = schedule):
<services>
<service autorun="true" execStart="/usr/bin/python2 scripts/rozvrh.py" name="rozvrh" />
</services>
In dialog, detect variables, pass them to service, and parse the call result to say answer:
u:(rozvrh) Pro jakou místnost bys chtěl znát rozvrh?
u1:({pro} {místnost učebnu} _~letter _~number) Podívám se na rozvrh pro $1 $2 ^call(Rozvrh.get_current_lesson($1, $2)) \pau=500\
c1:(In _* teaches _* course _*) V místnosti $1 je právě $3 s vyučujícím, který se jmenuje $2.
c1:(In _* currently _*) V místnosti $1 je právě $2
Note that in c1: we can use _* since this regular expression is matched against text from the service, not against human speech. The text can be in English (or even in non-language), the answer to humans is then specified in the concrete dialog topic, e.g. in Czech. Unfortunately, the documentation is not clear in what can and what cannot be matched by _* here, tests are needed with real data.
u1 detects letter and number (concepts defined earlier in dialog) and calls get_current_lesson(). This function return strings, that are parsed in dialog and answer is translated to each locale.
def get_current_lesson(self, letter, number):
room = letter + str(number)
lesson = self.rozvrh.find_current_lesson(room)
if lesson:
if lesson.teacher:
teacher = lesson.teacher.split(' ')[-1]
return "In %s teaches %s course %s" % (lesson.room, teacher, lesson.name)
else:
return "In %s currently %s" % (lesson.room, lesson.name)
Run script as service and use TTS in script
Detect variables in dialog, pass them to script and let script use TTS to say answer.
u:("[řekni ukaž zobraz najdi] {mi} [odjezdy spoje] ze zastávky _~station_name")
^call(DialogKordisbot.say_answer1($1))
Dialog detects word with station name and calls say_answer1(). No answer is passed back, answer is said directly in script.
def say_answer1(self, station):
#get data finalDepartures
answer_msg = "First line {} goes to {} at {}, second line {} goes to {} at {}, third line {} goes to {} at {}".format(finalDepartures[0][0], finalDepartures[0][1], finalDepartures[0][2], finalDepartures[1][0], finalDepartures[1][1], finalDepartures[1][2], finalDepartures[2][0], finalDepartures[2][1], finalDepartures[2][2])
self.s.ALAnimatedSpeech.say(answer_msg)
Testing a service with virtual robot
A service can be tested in the virtual robot settings.
- prepare an app with the service to test - you may start with the examples below or use the templater tool robot-jumpstarter (use a new name for your service instead of TweetyService):
ssh aurora cd /nlp/projekty/pepper/web/robot-jumpstarter python jumpstart.py python-service tweety-service TweetyService cp -a output/tweety-service ~/pepper/
Heretweety-serviceis the directory name of the application (and the app name),TweetyServiceis the API name of your service as it will be called from Python.
- copy the directory with the service app (e.g.
~/pepper/tweety-service) to your computer, where you run Choregraphe. All the following steps are done on this computer, not remotely via SSH. - start Choregraphe and run the virtual robot
- find out the port number of your virtual robot: click
and remember theIPandportfrom the table:
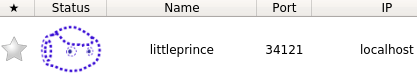
Here the virtual robot's address islocalhost:34121 - connecting to the Choregraphe virtual robot seems not to work in Windows environment, only in Linux.
For Windows, the virtual robot can be run via the NAOqi binary:
c:/Program\ Files/Softbank\ Robotics/Choregraphe\ Suite\ 2.5/bin/naoqi-bin
with the output saying[I] 1650614881.924666 23993 qimessaging.servicedirectory: ServiceDirectory listener created on tcp://127.0.0.1:9559 [I] 1650614881.925642 23993 qimessaging.transportserver: TransportServer will listen on: tcp://127.0.0.1:9559 [I] 1650614881.927379 23993 qimessaging.servicedirectory: Registered Service "ServiceDirectory" (#1) ...
Here the robot's URL is127.0.0.1:9559. - run your service in the virtual robot (Choregraphe must still be running, of course):
cd ~/pepper/tweety-service/app python2 scripts/tweetyservice.py --qi-url localhost:34121
The output should look like:[I] 1584373059.579170 4749 qimessaging.session: Session listener created on tcp://0.0.0.0:0 [I] 1584373059.579385 4749 qimessaging.transportserver: TransportServer will listen on: tcp://192.168.1.2:36873 [I] 1584373059.579394 4749 qimessaging.transportserver: TransportServer will listen on: tcp://127.0.0.1:36873
Keep this service running (in the background or foreground, i.e. use other shell/window for the
qiclicommands).
- now you can communicate with your running service in the same way as with all other API services on the real robot:
- use
^call(TweetyService.get())in a dialog - direct call in a Python Box code:
def __init__(self): self.tweety = ALProxy('TweetyService') def onInput_onStart(self): self.tts.say("číslo {}".format(self.tweety.get())) self.onStopped() #activate the output of the box - use the qicli command line tool:
with the output
alias qicli='"/opt/Softbank Robotics/Choregraphe Suite 2.5/bin/qicli" --qi-url localhost:34121' qicli info TweetyService qicli call TweetyService.get qicli call TweetyService.set 2 qicli call TweetyService.get
099 [TweetyService] * Info: machine f883b92e-3a87-44e5-aa70-4a3b78f4d937 process 4749 endpoints tcp://192.168.1.2:36873 tcp://127.0.0.1:36873 * Methods: 100 get Int8 () 101 reset Void () 102 set Void (Int8) 103 stop Void () ------------------------------------------------------- 0 null 2 - if the service uses Python packages from the Softbank
site-packages, the service needs before the firstimport:import sys sys.path.append('/opt/Softbank Robotics/Choregraphe Suite 2.5/lib/python2.7/site-packages')
- use
Example app
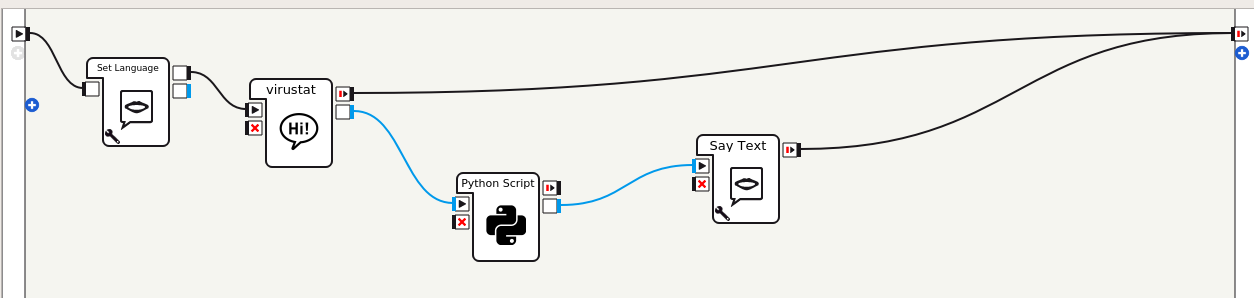
This application implements the option 1 of the two integration solutions mentioned above, i.e. it does not use a service, just simple dialog variables with standard Choregraphe box flow.
- Create new project in Choregraphe.
- As usual, add
Czechin project Properties. - Add
Set Languagebox and selectCzech. Warnings may appear when running this box on the virtual robot (ALSpeechRecognition is not available ...) but these are harmless now. - Right click the free area ->
Create a new box->Dialog... - in the Dialog ->
Add Topic- chooseCzechandAdd to the package content as collaborative dialog(allows to start the dialog just by talking to the robot) - Connect
onStart->Set Language->Dialog - Right click dialog box ->
Edit box. FindOutputsand click on+button.Name: country,Type: string,Nature: punctual
- In Project files double click on
virustat_czc.topand entertopic: ~virustat() language: czc u:(ahoj) ahoj, pro který stát tě zajímá statistika? u1:(Česko) dobrá, česko $country=Czechia u1:(Německo) dobrá, německo $country=Germany - Value of variable
$countrywill be sent to the output namedcountry. - Right click the free area ->
Create a new box->Python... - Find
Inputsand click on the Edit icon next toonStart. setTypeto String. - Find
Outputsand click on+button.Name: returnStat,Type: string,Nature: punctual - Connect
countryoutput of the dialog withonStartinput of the Python script. - Add
Say Textbox and connectreturnStatoutput of the Python script withonStartinput ofSay Textbox. - Connect
onStoppedoutput ofSay Textbox withonStopped.
- Double-click the Python script to edit the script, and exchange autogenerated script with the following:
class MyClass(GeneratedClass): def __init__(self): GeneratedClass.__init__(self) def onLoad(self): #put initialization code here pass def onUnload(self): #put clean-up code here pass def onInput_onStart(self, country): #self.onStopped() #activate the output of the box self.logger.info("start") self.logger.info(self.getStat(country)) self.returnStat(self.getStat(country)) def onInput_onStop(self): self.onUnload() #it is recommended to reuse the clean-up as the box is stopped self.onStopped() #activate the output of the box def getStat(self, country): import urllib2 url = 'https://opendata.arcgis.com/datasets/bbb2e4f589ba40d692fab712ae37b9ac_2.csv' response = urllib2.urlopen(url) csv = response.read() for line in csv.splitlines(): data = line.split(',') if data[3] == country: return 'Počet nakažených je '+data[7] - Download the sample application (virustat.zip), unzip it and open in Choregraphe.
Other example applications
Explore example applications in /nlp/projekty/pepper/myapps:
- kordisbot, Brno traffic dialog (runs own service
DialogKordisbot, needs to installBeautifulSoup,reuqestsandpyopensslin the service environment) - sport_bot, dialog about Premiere League results
- rozvrh, dialog about the faculty course schedule
[ previous part ] [ next part ]